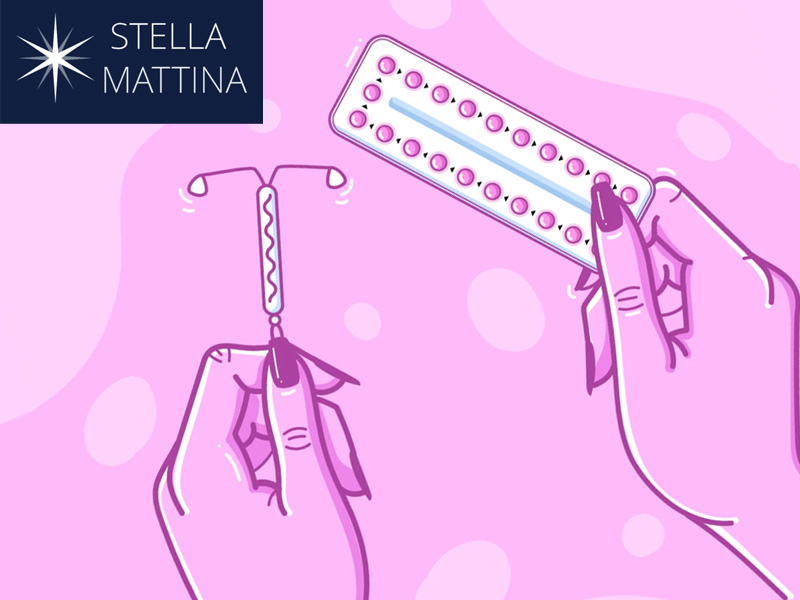
Choosing the right birth control method is a personal decision shaped by your health needs, lifestyle, and goals. Two popular options are the intrauterine device or IUD vs. birth control pill. Let’s explore how each works and what their benefits are for the different stages of your life.
But first, a quick summary of each kind.
IUD vs. Pill: Understanding How Each Method Works
An IUD is a small, T-shaped device that a healthcare provider inserts into your uterus. There are two types of IUD:
- Hormonal IUDs. These release a small amount of progestin, a hormone that thickens your cervical mucus to block sperm reaching an egg – and also, in some cases, prevents ovulation (eggs leaving your ovaries). Progestin also thins out the endometrium, or lining of the uterus, making periods very light or stop completely. They can last from 3 to 7 years, depending on the brand.
- Copper IUDs. These are the non-hormonal version. They release copper ions that create a toxic environment for sperm, preventing fertilization. They can be effective for up to 10 years.
Birth control pills, on the other hand, are oral contraceptives taken daily. They come in several forms, but the most common types are these:
Combination pills: They contain both estrogen and progestin, working together to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and thin your uterine lining.
Progestin-only pill: These low-estrogen birth control pills contain only progestin and are suitable for individuals sensitive to estrogen or who need a lower hormone dose.
Key Differences IUD vs. Birth Control Pill
When you’re deciding which contraceptive method to choose, keep in mind your lifestyle and health needs. Here are some factors that might help you decide:
Effectiveness
- IUDs are over 99% effective with typical use and require no daily maintenance once placed.
- Birth control pills are 99% effective if taken correctly – but decrease in effectiveness if you miss any!
Convenience
- IUDs are a “set it and forget it” option, remaining effective for several years.
- Birth control pills require daily commitment.
Duration
- IUDs offer long-term protection.
- Birth control pills are a short-term solution that can be easily discontinued.
Hormone Exposure
- Hormonal IUDs release localized hormones directly into your uterus, generally leading to lower hormone levels circulating in your bloodstream compared to other methods. It’s also possible that the progestin from an IUD can suppress your ovarian function and therefore also potentially lower your normal baseline.
- Birth control pills introduce hormones that can impact your whole body because they have to enter your body in higher amounts to reach the target.
Side Effects
Common side effects of IUDs include cramping and bleeding after IUD placement, especially within the first few months.
Birth control pills may cause side effects such as nausea, headaches, or, in rare cases, an increased risk of blood clots.
IUD vs. Birth Control Pill: Special Considerations for PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) often involves hormonal imbalances and irregular periods.
When considering IUD vs. birth control pill for women with PCOS, we have to understand how each method interacts with its symptoms.
Birth control pills are most commonly prescribed to help balance hormones, regulate periods, and manage symptoms like acne and excess hair growth.
Doctors will discuss the use of an IUD and PCOS management at the same time. If you prefer minimal side effects, a hormonal IUD can provide contraception and potentially reduce bleeding without impacting overall hormone levels as much as pills.
Choosing the Right Contraception Method at Different Life Stages
Your needs often change depending on your stage of life. When looking at birth control pills vs. IUD, factors like relationship status, career goals, family planning, and health conditions all play a role in determining which birth control method is the best fit.
But let’s look at the topic of IUD vs. birth control pill in general.
Teens and Early 20s
For teens and young women in their early 20s, the focus is often on reliable contraception that aligns with a busy or unpredictable lifestyle.
IUDs are highly effective with minimal maintenance, making them ideal if you’re looking for a long-term solution without a daily commitment.
Birth control pills are a great choice for young women who prefer a method they can easily start and stop. Combination pills can help regulate periods and control acne, a common concern in this age group.
Mid-20s to Early 30s
During this period, many women focus on career-building, travel, or personal goals, making reliable and convenient contraception essential.
IUDs offer years of hassle-free contraception. Because hormonal IUDs can also reduce – or even eliminate – monthly periods, they’re ideal if you want to avoid some of the monthly inconvenience and symptoms of menstruation.
Birth control pills offer a simple and effective way if you want flexibility or are maybe considering pregnancy in the near future.
30s to Early 40s
As women enter their 30s and early 40s, family planning becomes more prominent.
IUDs have no lasting impact on your fertility after removal – so they provide a reliable form of contraception while leaving open the option to start a family later on.
Birth control pills can be a suitable option if you’re intending to start a family soon, because they can be stopped as soon as you want to start conceiving.
Mid-40s and Beyond
For women in their mid-40s and older, contraception can serve multiple purposes beyond pregnancy prevention, such as managing menopausal symptoms.
Hormonal IUDs not only provide reliable contraception but can also help manage perimenopausal symptoms, such as heavy or irregular periods.
The combination birth control pill can help balance your hormones during perimenopause, offering relief from symptoms like hot flashes or mood swings. Low-estrogen birth control pills can also reduce the risk of blood clots, which becomes more of a concern with age.
Can Birth Control Pills Cause Infertility?
No. Birth control pills do not cause infertility. Once you stop taking them, your fertility typically returns quickly, though it may take a few months for regular ovulation to resume.
What Should I Do if I Miss a Birth Control Pill?
Missing a pill once in a while happens – we’re human! But it’s important to take it as soon as you remember. Missed birth control pill doses are a common reason for reduced effectiveness, as mentioned above.
Find the Right Birth Control for You With Stella Mattina
Ultimately, deciding between IUD vs. birth control pill depends on your health, lifestyle, and long-term goals.
At Stella Mattina, we’re passionate about women’s health and empowering you to make the right decision for you.
If you’d like us to help guide you to the most suitable choice for your body and life stage, contact the doctor of your choice in the location you prefer and let’s talk!
Dr. Krum is currently in practice in Arlington, TX. He received his undergraduate degree at Texas A&M University, then attended UTMB Galveston for medical school, finishing in 1986, completing his residency there in 1990. Providing a full range of obstetrical and gynecological care, he specializes in the treatment of endometriosis and robotic surgery. He arranges his schedule so that same-day appointments are usually available.
